Yesterday was the 327th anniversary of the Battle of the Boyne, when the forces of Protestant Britain defeated the Catholic Irishmen fighting for James II, rightful king of England, Scotland, and Ireland. It is a black day for many Catholics, in no small part because many of them descend from Irish communities that remember the oppression that followed under the penal laws. In Northern Ireland today, July 12th remains a divisive date marked by sectarian tensions and the triumphalist pageantry of the native Scotch-Irish Protestants. One wonders whether the new Conservative-DUP alliance in the Commons will have had any affect on the infamous marches of the Orange Order, founded in remembrance of today’s events.As cursed as the memory of the Boyne remains for Catholics today, it’s worth remembering that things were a bit more complex in the 17th century. I enjoy a good bit of Jacobite nostalgia as much as the next trad, but I also think a more honest assessment of history is worth exploring. Human life is a complicated thing, and the strange story of the Williamite War is riddled with contradictions.
Tremendous irony lies at the heart of the Boyne and what it represents. William of Orange, the stalwart champion of Protestantism, overthrew the Catholic James while secretly in league with Pope Innocent XI.

His Holiness, Innocent XI P.M. (Source).
Innocent’s political priorities centered on maintaining the balance of power in Europe. In 1690, that meant checking the bellicose Louis XIV. Ever since the marriage of Charles I and Henrietta Maria, the British Crown had been in an ever-closer relationship with France. James II was Louis’s only real ally, and Innocent knew it. The Pope also seems to have considered James a bit dull. He is known to have found his methods in the re-conversion of England more than a little imprudent (it was, in short, a massive failure of triangulation between the vitriolically anti-Catholic Whigs and the pro-Establishment Tories. James was not shrewd enough to manage the two, and ended up pleasing no one).
There was another threat on the table. The future of Catholic France was at stake. Louis XIV had, on the one hand, made moves designed to give him the appearance of Catholic zeal. The revocation of the Edict of Nantes, though not approved by the Pope, is perhaps the greatest example. More troublingly, Louis had rammed through the Four Articles that so antagonized the Papacy by more or less establishing Gallicanism throughout the land. Innocent fought against these measures.
Things came to a boiling point when the Pope, in league with almost all the crowned heads of Europe, clashed with Louis over who would fill the see of Cologne. When the election proved inconclusive, Innocent decided in favor of his own candidate. To quote the Catholic Encyclopedia: “Louis XIV retaliated by taking possession of the papal territory of Avignon, imprisoning the papal nuncio and appealing to a general council. Nor did he conceal his intention to separate the French Church entirely from Rome. The Pope remained firm.”
Enter the Dutch.

- Willem III, Prince of Orange, King of England and Stadtholder, by Godfried Schalcken. c. 1692-97. (Source)
It is unclear to what extent Innocent might have aided William of Orange. An old legend current at the time asserts that the Pope had financed the expedition with a secret loan of 150,000 scudi. As one reporter puts it, “The sum, equivalent to more than £3.5 million today, equalled the Vatican’s annual budget deficit.” There is, it seems, some truth to this statement. The legend has been supported by more recent research, such as that conducted by the fiction authors Rita Monaldi and Francesco Sorti. They uncovered evidence that corroborated the longstanding claims of other historians.
Which leads us to a singular painting by Pieter van der Meulen, The Entry of King William Into Ireland. It has played a controversial role in Northern Irish history. Purchased by the Unionist government of Ulster in 1933, it originally hung in the Great Hall of Stormont. After shifting locations several times, eventually the Rev. Dr. Ian Paisley (of all people) hung it in his office. It is presumably the only picture of the Pope in glory that Dr. Paisley ever liked.
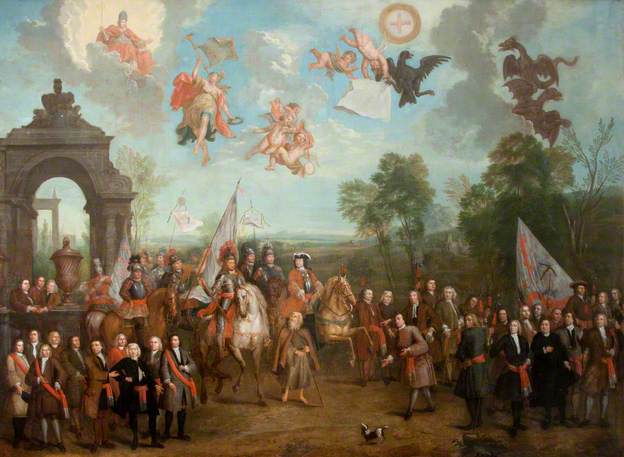

The Entry of King William Into Ireland, Pieter van der Meulen. (c) Northern Ireland Assembly; Supplied by The Public Catalogue Foundation. (Source).
So, why would a Pope act against a Catholic monarch—even covertly?
It seems that he sold Britain and Ireland to save France…and by extension, continental Catholicism. It was a gamble, and a costly one at that. But it seems to have worked in the short run. Although France would later see a terrible anti-Catholic upheaval of its own, Louis was forced to abandon his immediate moves towards schism. He did not become a French Henry VIII. Among all the terrible things that followed the Boyne, at least that one very important good came of it.