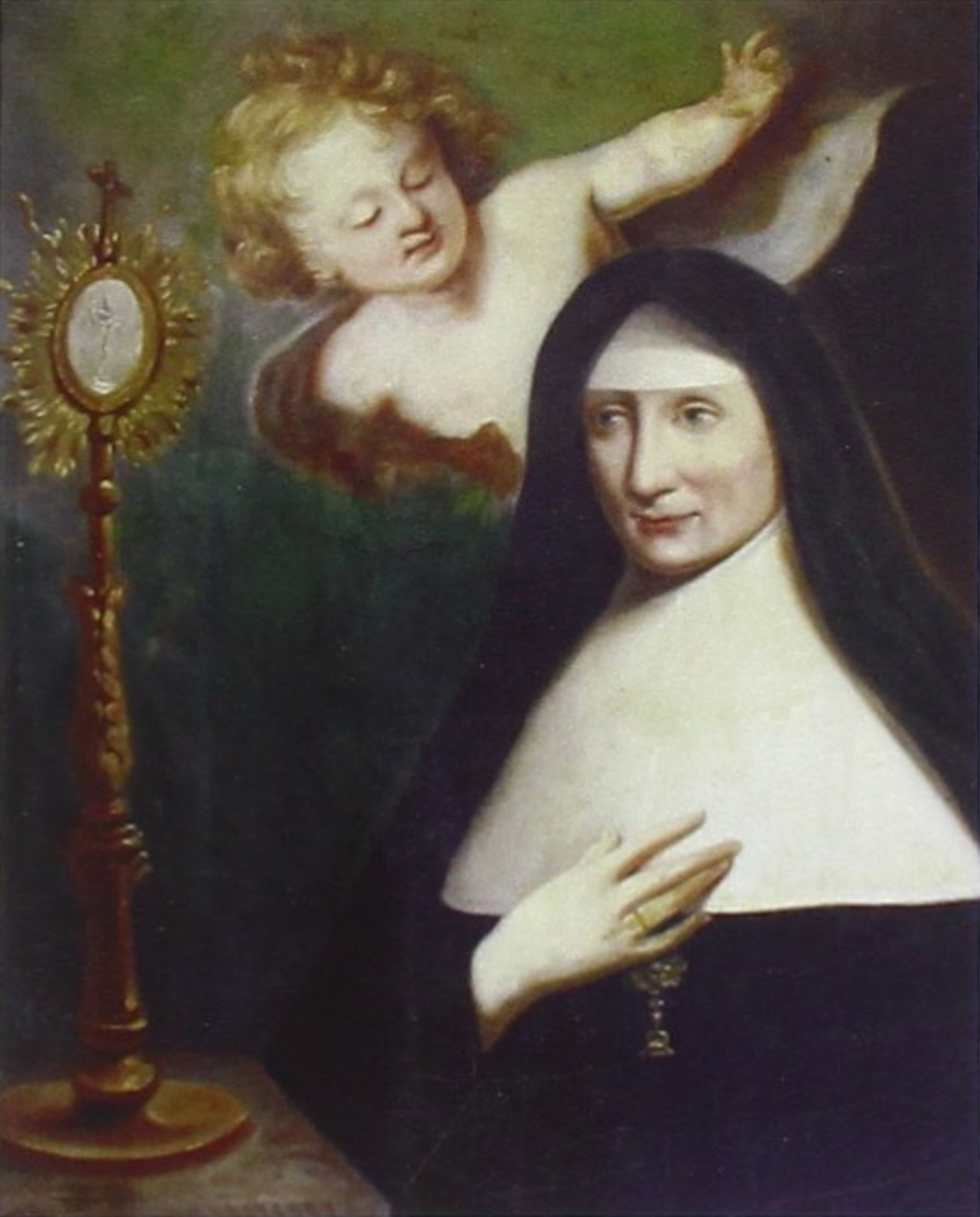
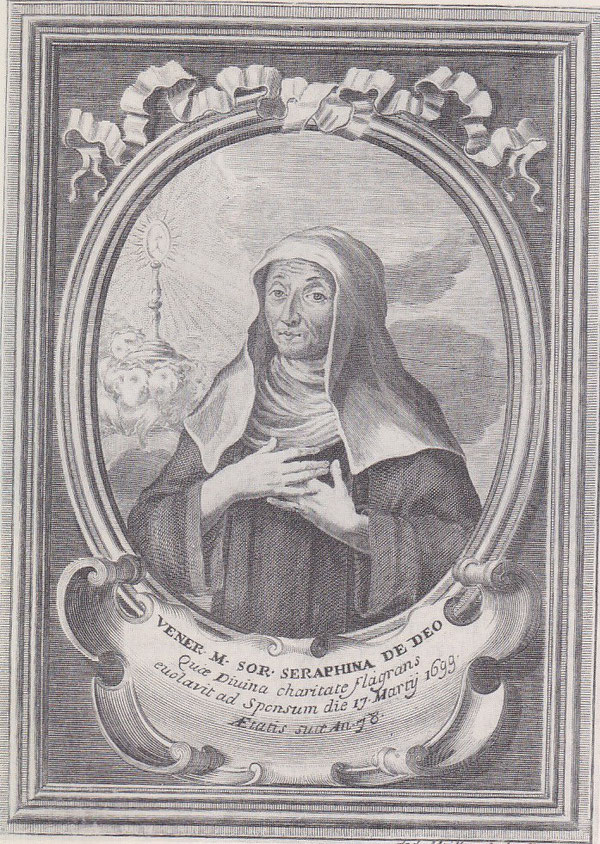
One of my favorite essays to write on this blog so far has been my study of the way that St. Philip Neri embodied certain Benedictine qualities. In that piece, I argue that sometimes we can gain a deeper understanding of a saint by looking at their likenesses with saints of a different religious family or by the influence of other saints in their lives. As an extension of that essay, I’d like to introduce my readers to a Venerable whom they have probably never heard of, one who followed St. Philip in a very Benedictine spirit: the Venerable Serafina di Dio, O.C.D.
The Life of a Mystic
Prudenza Pisa was born in the Kingdom of Naples in 1621. She clashed with her father at a young age when she refused to marry the young man he had chosen as her husband. She also cut her hair and donned pentiental garb. These actions did not go over well, and she soon found herself expelled from the household. Prudenza resided during this rather fraught period in what was essentially the family chicken coop. Yet she grew closer to her mother, who brought her meals secretly. Prudenza saw these sufferings as an opportunity for growth in trust of God. She also set herself to the good works of visiting the sick. In the Neapolitan Plagues of 1656, she continued her ministry even as the illness claimed her beloved mother. Her behavior at this terrible juncture was edifying:
Seraphina prepared her mother for death and actually closed her eyes when she died on August 5th 1656. Christian burial was not allowed during the plague. With her own hands, she dug a shallow grave in the backyard and personally buried her mother.
Yet her active life was soon to draw to a close. One of her uncles, a prominent priest, died of the same plague. He had been planning to found a convent of enclosed nuns on Capri. She carried on this noble work after his departure. She gathered together various companions from Naples and, on 29th of May, 1661, took the habit of the Discalced Carmelites at Naples Cathedral. It was then that she took the name of Serafina of God. Later that year, the community moved to Capri. Their residence soon proved inadequate, and they constructed a much larger monastery dedicated to the Most Holy Savior. Mother Serafina’s leadership bore fruit in another six Carmelite convents in the Kingdom of Naples, a remarkable flourishing clearly drawing its power from the Holy Ghost.

The (very Dominican) arms of Pope Benedict XIII, friend of Ven. Serafina di Dio (Source)
Ven. Serafina was not without trials. Although she wrote an attack on Quietism, she was herself accused of this noxious heresy. For
six years, the Inquisition conducted an investigation into her writings and activities. For two, she was
confined to her cell without the benefit of Holy Communion. But at last, her name was cleared, in no small part because of the intervention of her friend, Archbishop Vincenzo Maria Orsini, the future Pope Benedict XIII.
There can be little doubt that these troubles arose from within her own religious family. Although Mother Serafina was entirely blameless in conduct, her manner of spiritual leadership won her many enemies among her more lax daughters. Perhaps some of the trouble could have been anticipated from the fact that her recruits were customarily drawn from the ranks of the Neapolitan aristocracy, not a class generally known for its ascetic rigor. The Carmelites treated their foundress poorly. For example, while Serafina was ill in her confinement, she begged to see some of the sisters. They did not come. Yet the patience with which she bore these final trials remains exemplary. As one biographer notes, “Two days before she died she asked the Prioress to look after the sisters who had been so contrary to her, making excuses for their behavior.” This mercy converted the hard of heart, for, as the same writer says, “After her death on March 17, 1699, some of the sisters who were most against her became some of the most enthustiastic promoters of her Cause.”
Spiritual Daughter of St. Philip Neri
An heir of the Tridentine reform, the Ven. Serafina was a great admirer of St. Teresa of Avila, whom she endeavored to emulate in all things. She was a prolific writer, composing at least 2,173 letters and enough theological writing to fill 22 books. Some of her topics included:
-the prayer of faith
-mental prayer
-the love of God and the practice of the divine presence
-the common life
-conformity to the will of God.
Alas, I don’t believe any of these have been translated into English. Perhaps some intrepid early modernist will someday render these works into the Anglo-Saxon tongue.
Serafina was also a visionary mystic. She went about life with a constant ability to fall into meditation. In Serafina’s own words:
“…Anything I looked at I was able to turn into a meditation… When I saw it raining, I thought of the refreshment which the rain brought to the earth and that without it the earth would be arid. I would say: ‘If the water of divine grace did not fall on the soul, it would dry up without providing the fruits of good works.’ … The sight of fish swimming in the sea made me remember how the saints are immersed in God… And in such wise everything, even the slightest things, served me for my spiritual nourishment.”
The greatest misfortunes could not turn her from the praise of God. For in all things, she perceived the benevolent Providence of God. Her unfailing rule was that “All that God did and allowed was beautiful, good, ordered for our good.” Even the terrible things in life thus became for Serafina an occasion of magnification and blessing.
Serafina was also a visionary mystic. At one point, “She was so overwhelmed with her vision of the Godhead that she wondered what else could be reserved for her in heaven.” The experiences she was granted were extraordinary, though she took pains to keep them discreet. Yet we do have letters attesting to some of her ecstasies.
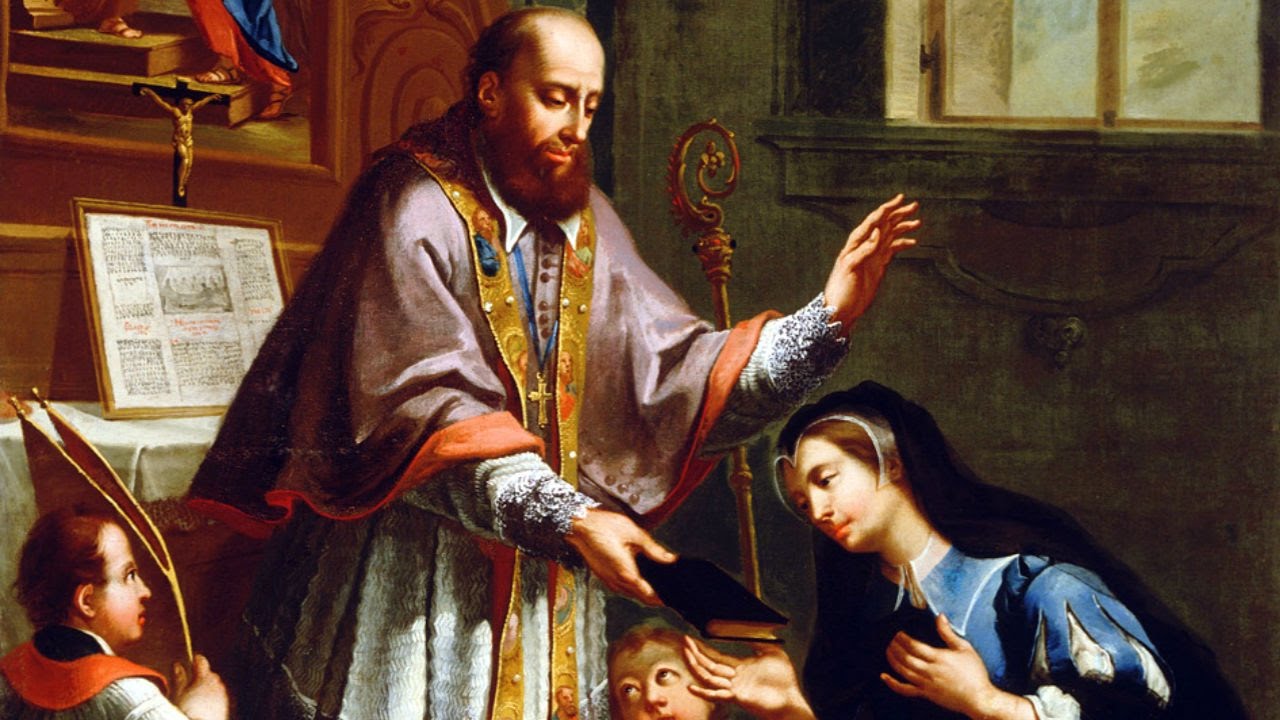
One figure who emerges as particularly important in her religious life is St. Philip Neri. The Oratorian Fr. Francesco Antonio Agnelli tells us that she honored St. Philip by, for instance, devoutly kissing the feet of the crucifix thirty-three times in his honor; she was repaid for this act of love with a vision of the glorified St. Philip prostrate and kissing the feet of Jesus thirty-three times in her name (Agnelli 194).
Serafina’s spiritual father was Fr. Vincenzo Avinatri of the Naples Oratory. She wrote him letters describing the visions she had of St. Philip. In one such letter, she reports that
“I saw the Saint, with the great Mother of God, in a flame of fire, and surrounded with light…with a sweet countenance, he told me many beautiful things…He showed me what his sons ought to be, and the dignity of the Congregation, made, so to speak, in the likeness of God and of the three Divine Persons, and especially of the Person of the Holy Spirit…Without speaking, he had explained to me the perfection we must have in order to be sons of light. It would be a monstrous thing if fire generated snow, if light brought forth darkness, if crystal produced mud…How much greater wonder would it be, if in any of the sons of St. Philip, who are called sons of the Holy Spirit, there should be any defect!” (qtd. in Agnelli 195-96)
In another vision that came to her on the vigil of St. Philip’s day, she was carried way into a heavenly rapture and saw the Saint aflame with a supernal light. And in view of St. Philip, she saw her own heart on fire, as well. But it did not glow as brightly as his; therefore, she prayed to the Saint that she might receive a more perfect and ample share of Divine Love. As Agnelli describes it,
Then the Saint united his heart with hers, and thus united they sent forth a great flame; she felt so much love that she could not express it, and the Saint invited her to rejoice in the presence of the Lord, and to sing His praises, desiring her to repeat with him these words, Sanctus, Sanctus, Sanctus, Magnus Dominus et laudabilis nimis [Holy, holy, holy, great is the Lord and worthy of all praise], adding that it is impossible to find in the most devout Canticles words more pleasing to God. (Agnelli 194-95).
She was thus adopted by the saint as a kind of daughter in the Spirit. She also looked upon Oratorians as her own sons. This spiritual affinity was later attested by a physical resemblance with St. Philip. When an autopsy was conducted on Mother Serafina’s body, the examiners found signs of transverberation in her heart.
It may seem odd for a visionary to become so friendly with St. Philip and his sons. After all, St. Philip himself was notorious for his skepticism when it came to visions. He had treated the Ven. Ursula Benincasa with unrelenting verbal abuse to test her inspiration – a test she passed, even if the holy man never quite came around to endorsing her. St. Philip taught that, “As for those who run after visions, dreams, and the like, we must lay hold of them by the feet and pull them to the ground by force, lest they should fall into the devil’s net.” Though a man of tremendous supernatural gifts himself, he knew that the spiritual world was a minefield of dangers. False visionaries abounded in his day, and his prudent words have retained their perennial wisdom down into our own era.
To properly understand the nature of Ven. Serafina’s visionary mysticism, and why we can properly say it breathes of a Philippine spirit, we must look at it in the context of her leadership of a Carmelite monastery.
A Liturgical Mysticism
The troubles in Serafina’s life began because of her governance. As one biographer has it,
As often happens, Sr. Seraphina’s strongest talents and graces became her heaviest crosses. In her foundations she shared her convictions about religious life with her sisters. She firmly believed that the best guarantee of authenticity of one’s religious experience was a dogged faithfulness to the traditional forms. She was immersed in the church’s liturgy, the celebration of the Eucharist, the Divine Office, the liturgical year, and the feasts of the Saints. She was often led to intimate communion with Christ Jesus at the liturgy beginning with the midnight office. She also stressed the need for silence and solitude as requisites for prayer. [emphasis mine – RTY]
Her tenacious devotion to the traditional forms of worship and to the great prayer of the Church, the Liturgy and Divine Office, shows that the Ven. Serafina was in every way a monastic. Indeed, these salutary measures evince a Benedictine sensibility.
Her ecstasies were not a superfluous and shallow add-on to this liturgical life. She built the house of her prayer upon the rock of tradition, and it was illumined with the uncreated light of the Holy Ghost.
Serafina’s mystical life was tied to her experience of the liturgical calendar. For instance, any of her most profound encounters with St. Philip took place on the vigil and day of his feast (Agnelli 194-95). A cynic would see in this timebound quality a mark of the merely human dimension of religion, a fine example of confirmation bias. But those who have learned of divine things will discover a deeper reality. In Serafina they will see a soul that has grown attuned to the Wisdom of God, made manifest in time through the Incarnation of Christ and the Liturgy of the Church.
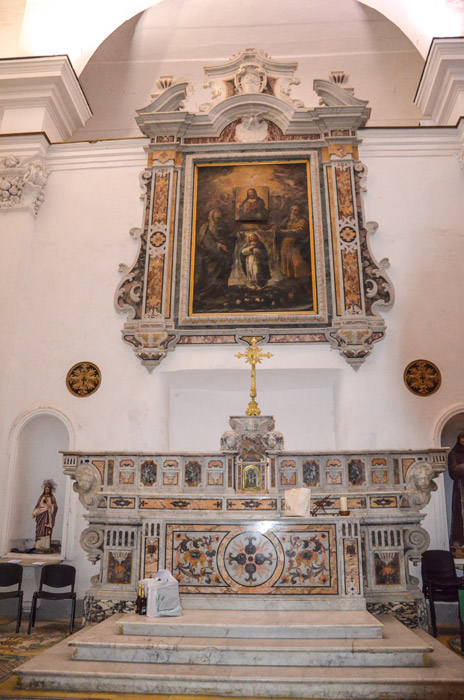

High Altar of the Chiesa Santissimo Salvatore, Capri. Although it has not been a Carmelite monastery since Napoleonic times, this is the altar where the Ven. Serafina would have received communion. (Source)
These are quintessentially sound foundations for the spiritual life. Her strictly liturgical and monastic way engendered serious opposition among her daughters, but it also gave her the strength to bear that opposition with true Christian patience. One can only imagine the terrible suffering that two years without the Blessed Sacrament must have inflicted on such a soul. Yet, by grounding herself in the Liturgy, she was able to nourish that innate trust in Providence already evident in her earliest days. Surely, that sustained her in the darkest days of her old age.
The Long Road to Sainthood
It seems somehow appropriate that, as an adopted daughter of St. Philip, the Ven. Serafina should not yet have been canonized. Many of his spiritual children have had a similar fate. Witness the stalled cases of Ven. Cardinal Cesare Baronius, Bl. Juvenal Ancina, Bl. Anthony Grassi, and Bl. Sebastian Valfre, just to name a few of the many early modern Oratorians who have not yet reached the highest altars of the Church.
Still, we can pray that this Carmelite mystic will one day be recognized as the saint she was. Let us beg her intercession and emulate her profound devotion to the Liturgy of the Church.
UPDATE: A Carmelite friend pointed out to me that Ven. Serafina was in fact not subject to the jurisdiction of either Carmelite order, essentially running independent Carmelite conservatories of oblates in the Discalced habit, following an adaptation of St. Teresa’s constitutions. She was a sort of Carmelite version of St. Francesca Romana. More info can be found in the works of Smet. As such, any use of the Carmelite letters after her name may be inappropriate, but given a) the unusual nature of the case, and b) the difficulty of changing my title and thus invalidating links, I have decided to keep my text as is and merely add this disclaimer.

May the Ven. Serafina di Dio pray for us! (Source)